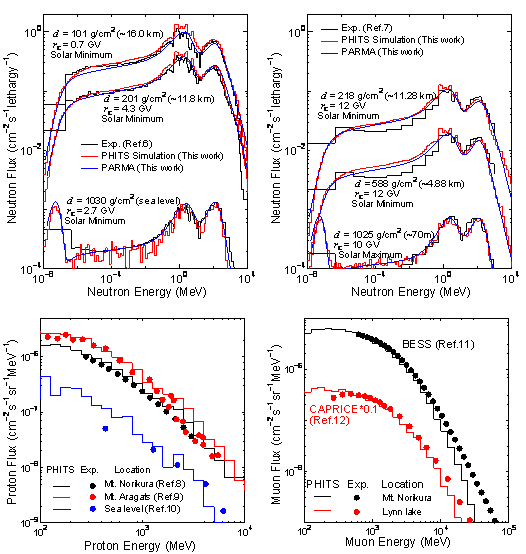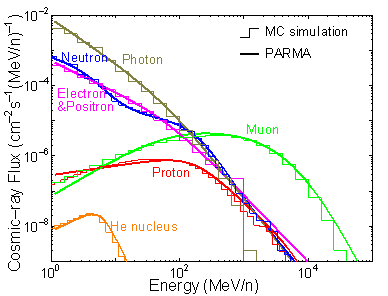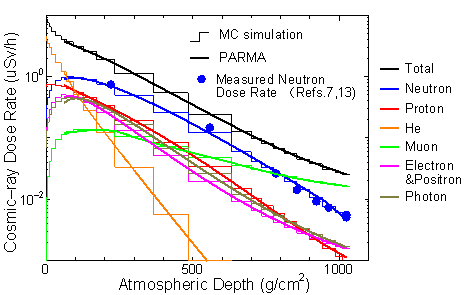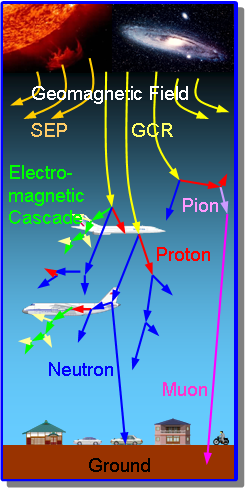
Fig.1 Schematic view of the atmospheric propagation of cosmic-ray
Furthermore, radiation protection for aircrews against the terrestrial cosmic-rays has been intensively discussed since the publication of ICRP60 in which the aircrew exposure is recognized as occupational hazard. Development of aircrew-dose calculation code is the one of the most important issues in the discussion. Establishment of reliable model for calculating the cosmic-ray spectra for any global conditions is the key issue in the development. It should be also noted that estimation of the spectra is of great importance from the viewpoint of geoscience.